describing distribution of box plots skew The box plot will look as if the box was shifted to the left so that the right tail will be longer, and the median will be closer to the left line of the box in the box plot. If the distribution is skewed to the left, most values are 'large', but there are a .
A vertical milling machine, also known as a vertical machining center or CNC vertical milling machine, is a versatile machining tool. Its main feature is a vertically oriented spindle, which can fix and rotate cutting tools, allowing them to .
0 · vertical box plot skewness
1 · skewed right box plot
2 · skewed left whisker plot
3 · right skewed box plot vertical
4 · positively skewed box plots
5 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
6 · left skewed plot
7 · box plot negatively skewed
Definition of a Septic D-Box: a septic distribution box is a container used to receive septic system effluent from a septic tank and to re-distribute the effluent into a network of attached drain-field or soakaway bed absorption trenches & pipes.
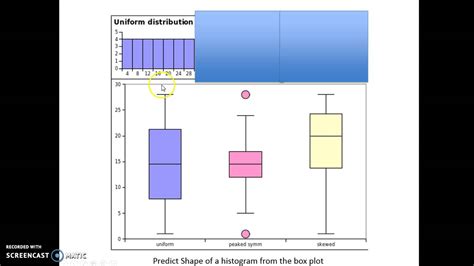
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum . In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or .
To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, .The box plot will look as if the box was shifted to the left so that the right tail will be longer, and the median will be closer to the left line of the box in the box plot. If the distribution is skewed to the left, most values are 'large', but there are a .
vertical box plot skewness
Two of such metrics are skewness and kurtosis. You can use them to assess the resemblance between your distributions and a perfect, normal distribution. By finishing this article, you will learn in detail: Let’s get started! . Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to analyze them. Let’s start by contrasting characteristics .
sentinel steel security cabinet key
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score. In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or symmetrical, provides crucial insights into data characteristics.To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.
skewed right box plot
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .The box plot will look as if the box was shifted to the left so that the right tail will be longer, and the median will be closer to the left line of the box in the box plot. If the distribution is skewed to the left, most values are 'large', but there are a few exceptionally small ones.
Two of such metrics are skewness and kurtosis. You can use them to assess the resemblance between your distributions and a perfect, normal distribution. By finishing this article, you will learn in detail: Let’s get started! What is Skewness? Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.
In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to analyze them. Let’s start by contrasting characteristics of the symmetrical normal distribution with skewed distributions. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.
In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or symmetrical, provides crucial insights into data characteristics.
To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .The box plot will look as if the box was shifted to the left so that the right tail will be longer, and the median will be closer to the left line of the box in the box plot. If the distribution is skewed to the left, most values are 'large', but there are a few exceptionally small ones. Two of such metrics are skewness and kurtosis. You can use them to assess the resemblance between your distributions and a perfect, normal distribution. By finishing this article, you will learn in detail: Let’s get started! What is Skewness?
septic distribution box speed control
Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.
skewed left whisker plot
septic alarm junction box
septic system distribution box replacement cost
A solar panel junction box is a crucial component of a solar panel system. It connects electrical components in the solar panel. It ensures that the generated electricity is distributed.
describing distribution of box plots skew|vertical box plot skewness